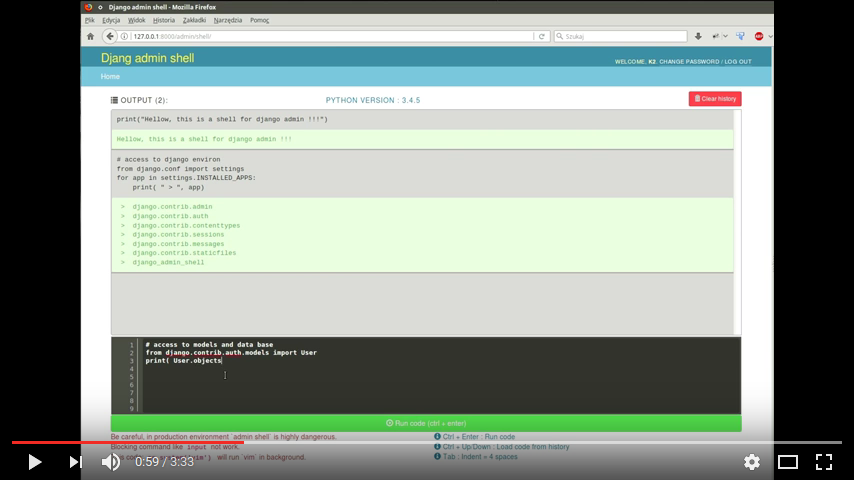
django-admin-shell
Django application can execute python code in your project\'s environment on django admin site. You can use similar as [python manage shell]{.title-ref} without reloading the environment.
-
- Tested by tox with:
-
- Python : 3.7, 3.8, 3.10
- Django : 2.0, 2.1, 2.2, 3.0, 3.1, 3.2, 4.0, 4.2
-
- Require:
-
- Django >= 1.10
-
- Tested on browsers
-
- OK - Chromium 108 - Ubuntu 20.04
- OK - Firefox 112.0.2 - Ubuntu 20.04
- OK - Chromium 89 - Ubuntu 18.04
- OK - Firefox 87.0 - Ubuntu 18.04
- OK - Chromium 79.0 - Ubuntu 18.04
- OK - Firefox 72.0.2 - Ubuntu 18.04
- OK - Firefox 50.1.0 - Ubuntu 14.04
- OK - Firefox 31.1 - CentOS 6.4
- OK - Chromium 53.0 - Ubuntu 14.04
- OK - Microsoft Edge 38 - Windows 10
- OK - Internet Explorer 11.0 - Windows 8.1
- OK - Internet Explorer 10.0 - Windows 7
- OK - Internet Explorer 9.0 - Windows 7
- ERR - Internet Explorer 8.0 - Windows 7 (javascripts not working / console work properly)
Screens
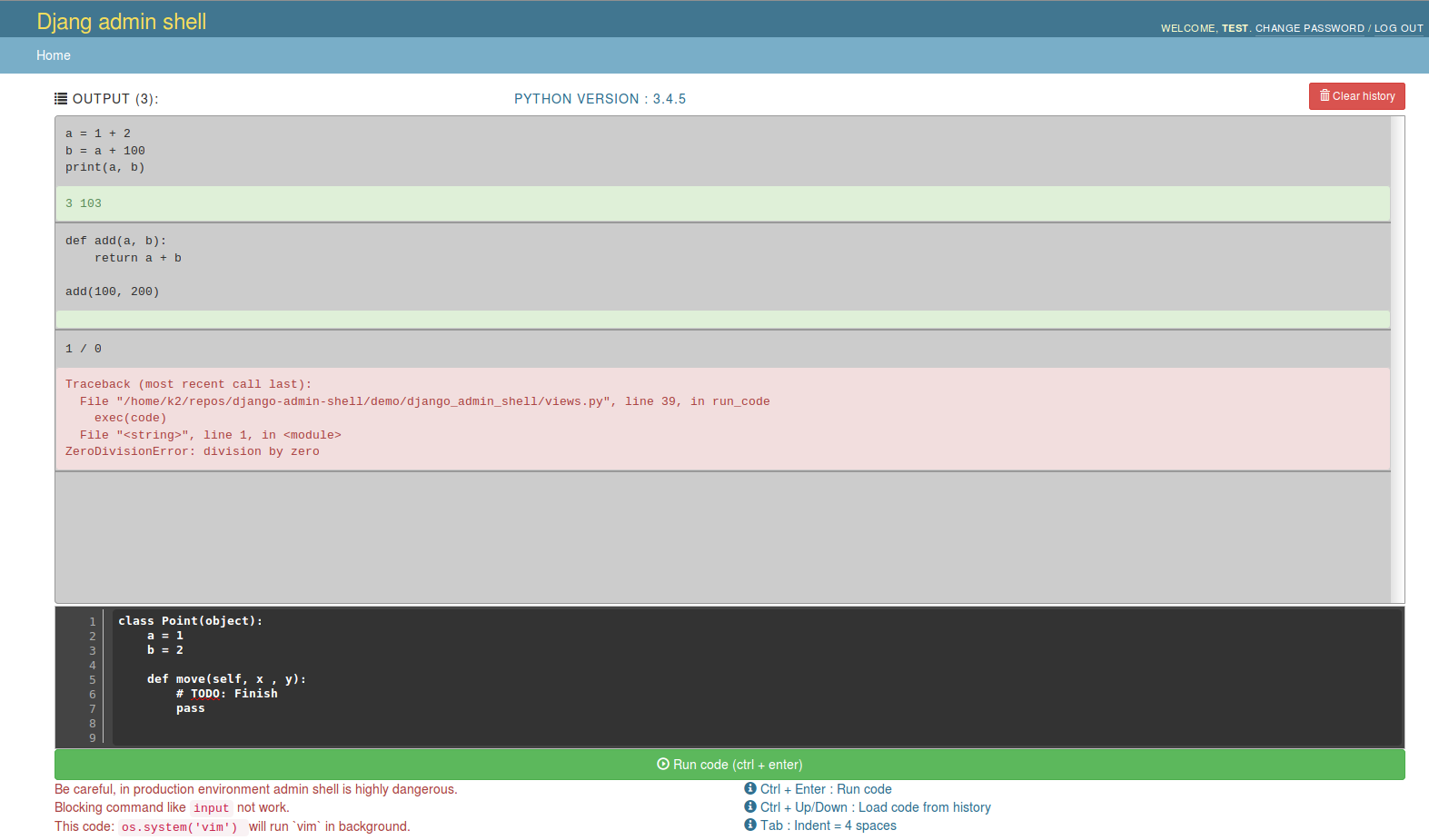
Shell in action
Install
-
Install:
pip install django-admin-shell or pip install git+https://github.com/djk2/django-admin-shell.git or after download zip pip install django-admin-shell.zip -
Add [django_admin_shell]{.title-ref} to your INSTALLED_APPS setting
settings.py :
INSTALLED_APPS = [ ... 'django_admin_shell', ... ]
- Add the [django_admin_shell]{.title-ref} urls to your root url patterns (above admin/) :
urls.py :
urlpatterns = [ re_path(r'^admin/shell/', include('django_admin_shell.urls')), ... re_path(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls), ]
Usage
- shell is available on url: /admin/shell
- On default settings user must be authenticated to django admin site and User must have superuser permission and DEBUG mode must be set on True.
::: note ::: title Note :::
Make sure that in your project session is enable
More about session and how enabling session read here : https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/dev/topics/http/sessions/
Usually default session in django project is enable :::
Demo
Try [django-admin-shell]{.title-ref} using simple demo app:
-
Clone project
-
Go to [demo]{.title-ref} directory:
cd django-admin-shell/demo
-
Install requirements:
pip install -r requirements.txt
-
Run demo project
./manage.py runserver
-
Go to \"http://127.0.0.1:8000/admin/shell\" and login to [admin]{.title-ref} user with password [admin]{.title-ref}
Settings
ADMIN_SHELL_ENABLE
type : bool
default : True
If shell is enable or disable. When application is disable then url: /admin/shell return Http404 Not found
ADMIN_SHELL_ONLY_DEBUG_MODE
type : bool
default : True
If flag is set on True, then shell is available only in DEBUG mode.
If debug mode is required and debug mode is disabled then url: /admin/shell will return Http 403 Forbidden
ADMIN_SHELL_ONLY_FOR_SUPERUSER
type : bool
default : True
If flag is set on True, then shell is available only for user with superuser permission.
If superuser is required and user not have permission then url: /admin/shell will return Http 403 Forbidden
ADMIN_SHELL_OUTPUT_SIZE
type : integer
default : 250
Flag determines how many outputs can be remember.
ADMIN_SHELL_SESSION_KEY
type : string
default : django_admin_shell_output
Name for key in session where is stored history last executed codes.
ADMIN_SHELL_IMPORT_DJANGO
type : bool
default : True
If flag is set on True, then useful libraries and packages from Django will be automatically imported to shell. For example: [from django.conf import settings]{.title-ref}, so in shell you have directly access to attributes from this module (e.g [settings.INSTALLED_APPS]{.title-ref}). List of automatically imported modules is displayed on top of console (screen below). If you want disable auto import for django packages, set this flag to [False]{.title-ref}.
Nont: If during import occurred error `ImportError` then this module will be omitted.
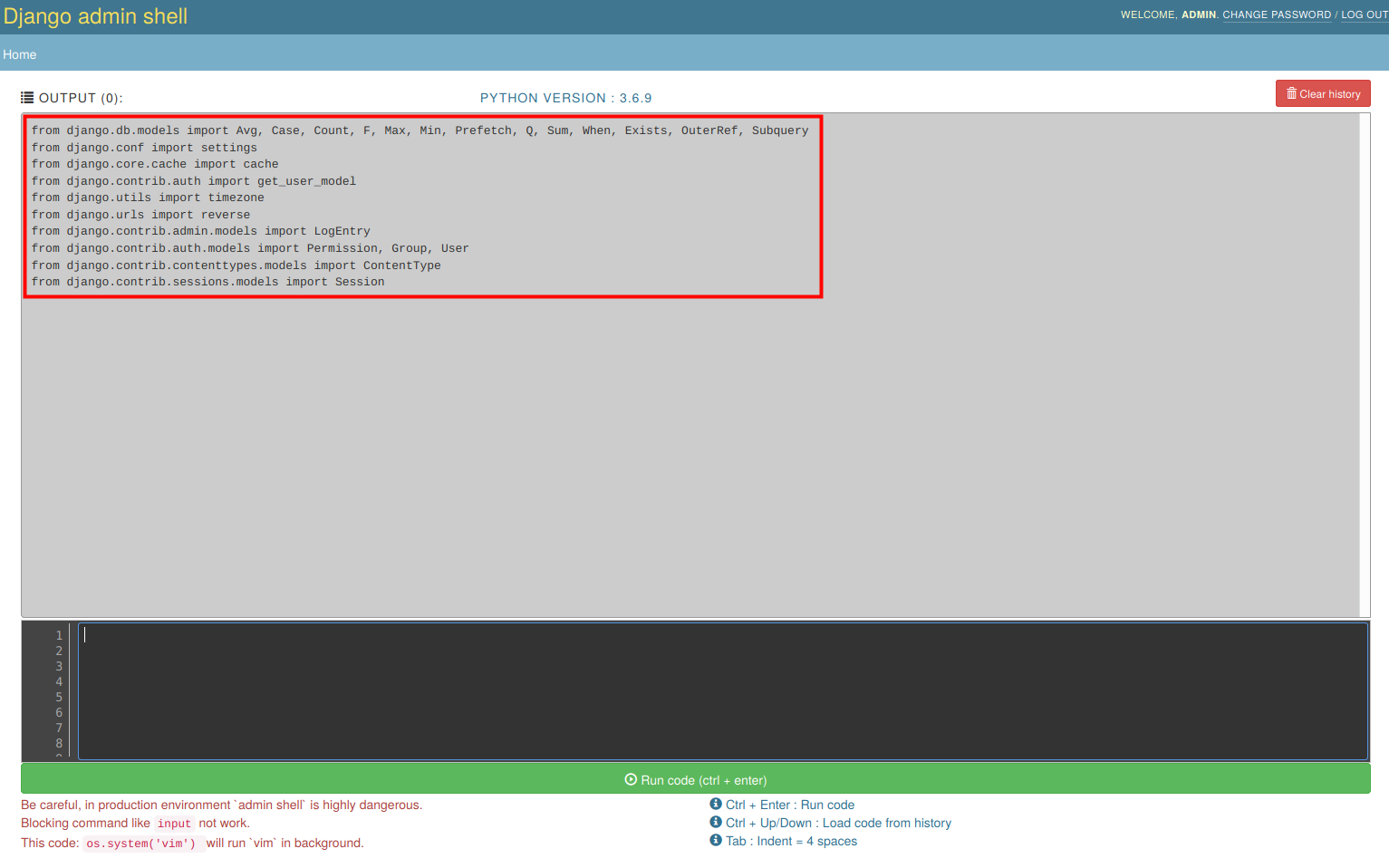
ADMIN_SHELL_IMPORT_MODELS
type : bool
default : True
This flag is similar to [ADMIN_SHELL_IMPORT_DJANGO]{.title-ref} but regarding auto import of models from all registered applications. If flag is set on True, then models from all apps will be automatically imported to shell. For example: [from django.contrib.auth.models import Permission, Group, User]{.title-ref}, so in shell you have directly access to this classes. List of automatically imported models is displayed on top of console. If you want disable auto import for models, set this flag to [False]{.title-ref}.
Nont: If during import occurred error `ImportError` then this module will be omitted.
ADMIN_SHELL_CLEAR_SCOPE_ON_CLEAR_HISTORY \^\^\^\^\^\^\^\^\^\^\^\^\^\^\^\^\^\^\^\^\^\^\^\^\^\^\^ type : bool
default : False
This flag is used to enable the gargabe collector on the declared variables from the shell execution when the \"clear history\" is executed. If this flag is set to [True]{.title-ref}, then all the declared variables will be ERASED and FREED from memory on runtime when \"clear history\" is used. If you want to persist indefinitly all declared variables on the shell, set this flag to [False]{.title-ref}.
BEWARE: leaving this disabled is not recomended on production code!
Code examples
-
show django settings:
from django.conf import settings for key in dir(settings): val = getattr(settings, key, None) print(key, "=", val) -
run command in operating system and take output:
import os os.system('date > /tmp/admin_console.tmp') os.system('echo ------- >> /tmp/admin_console.tmp') os.system('who >> /tmp/admin_console.tmp') os.system('echo ------- >> /tmp/admin_console.tmp') os.system('ps aux | grep python >> /tmp/admin_console.tmp') with open('/tmp/admin_console.tmp', 'r') as f: print(f.read()) -
run big python code (get python source from website):
import requests req = requests.get('http://foo.bar.com/example.py') if req.status_code == 200: code = req.text print(code, '\n------------\n') exec(code)
Useful for me:
- https://docs.djangoproject.com/
- https://jquery.com/
- http://alan.blog-city.com/jquerylinedtextarea.htm